Cell based architecture
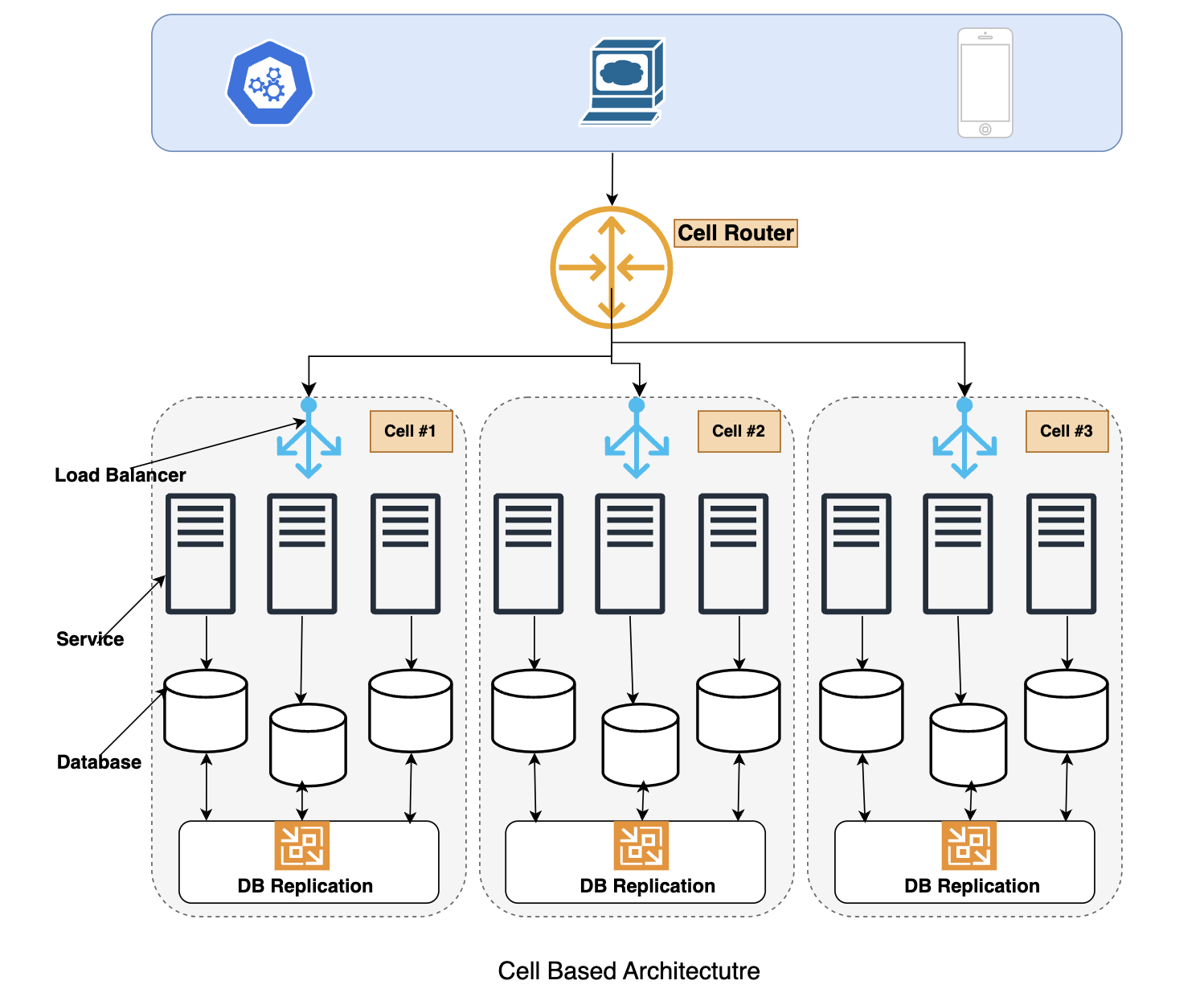
Bulkhead or Cell-based architecture is an architectural pattern adopted for constructing highly available, scalable, and fault-tolerant enterprise applications.
The concept of the bulkhead pattern draws inspiration from the architecture of ship hulls, wherein the hull is divided into multiple cells or sections to prevent the entire ship from sinking if one section is damaged.
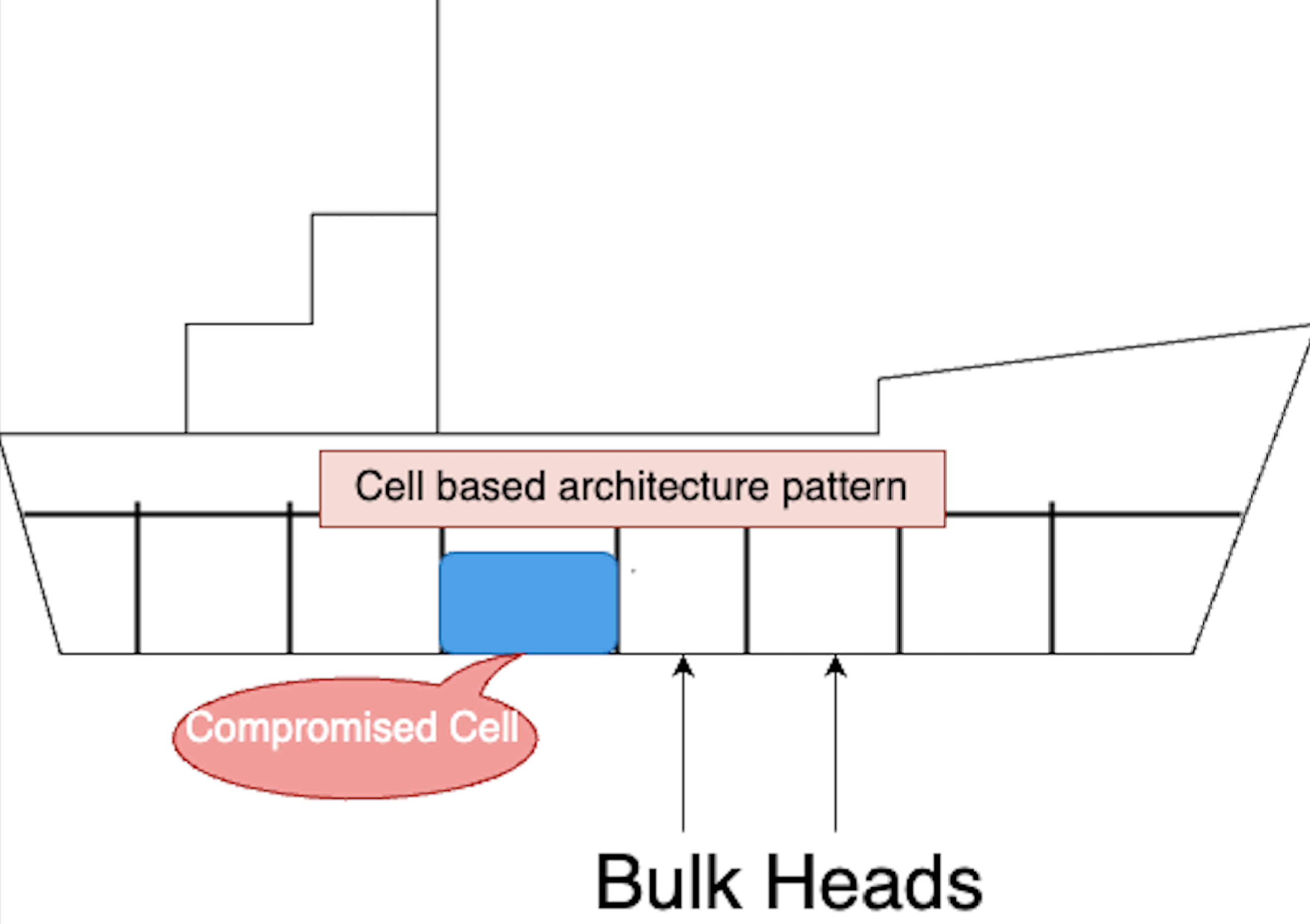
Vertical Partitioning of Walls dividing the Ship’s hull
In the bulkhead architecture approach, ships manage the risk of sinking by isolating compromised compartments. The vertical partitioning of walls divides the ship's interior into self-contained, watertight compartments, aiming to contain a hull breach within a specific section of the ship.
A similar concept is applied when designing scalable enterprise applications having dynamic workload, known as cell-based architecture.
Key Components of Cell Based Architecture
Cell Router
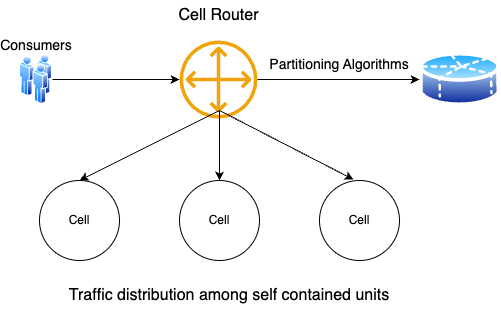
A cell router is a key component in a cell-based architecture. Traffic to every individual cell is routed through cell router. If a cell fails, only the traffic directed to that cell will be impacted. In short impact on the system will be minimal. The cell router is responsible for receiving the request, determining their destination based on cell partitioning algorithms, and then forwarding them towards the destination cell.
Blast Radius
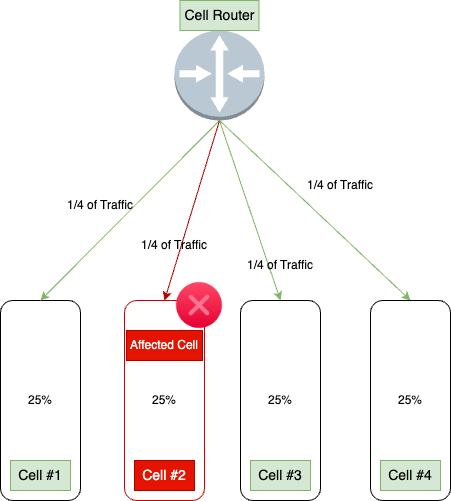
Represents the area or range of systems, components, or processes that may be affected directly or indirectly by a single cell failure event. For example, if a system is built with four cells and any service in a cell goes down only the 25% of traffic will be affected. So, the blast radius is approximate 25% here.
Traffic distribution
Cell router plays a critical role in orchestrating traffic distribution among cells in cell-based architecture. Traffic distribution works by routing incoming requests to the appropriate cell or service instance based on predefined routing rules or policies. The cells get partitioned using a partition key. A simple or composite partition key can be used to distribute the traffic between cells. the partitioning strategy could be ranging partitioning, hash partitioning, or list partitioning. The chosen partitioning strategy will influence how the partition key is used to distribute traffic across partitions.
Self-Contained Unit (Cell)
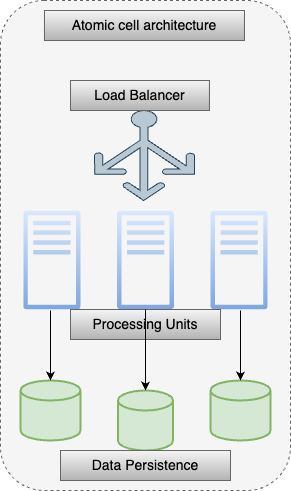
Complete in itself modules are the first-class citizen of any cell-based architecture. Such modules are the one which serves the logical / business purpose of a feature or service along with non-functional entities around it. Such as API’s, load balancer and database. In short, a cell in a cell-based architecture is self-contained and self- sustainable instance of an application which can be deployed, scaled, and observed independently. Cells are isolated with each other at logical level, failure of a cell does not affect other cells and reduces the overall impact to software. With the cell-based architecture a cell does not share encompassed services state with other cells in the system.
Cell Health Check
Before forwarding the request, the cell router layer may perform health checks on the target cell or service instance to ensure that cell can handle the request. If the target instance is unhealthy or unavailable, the router may reroute the request to a healthy cell or trigger automatic recovery mechanisms.
Database Replication
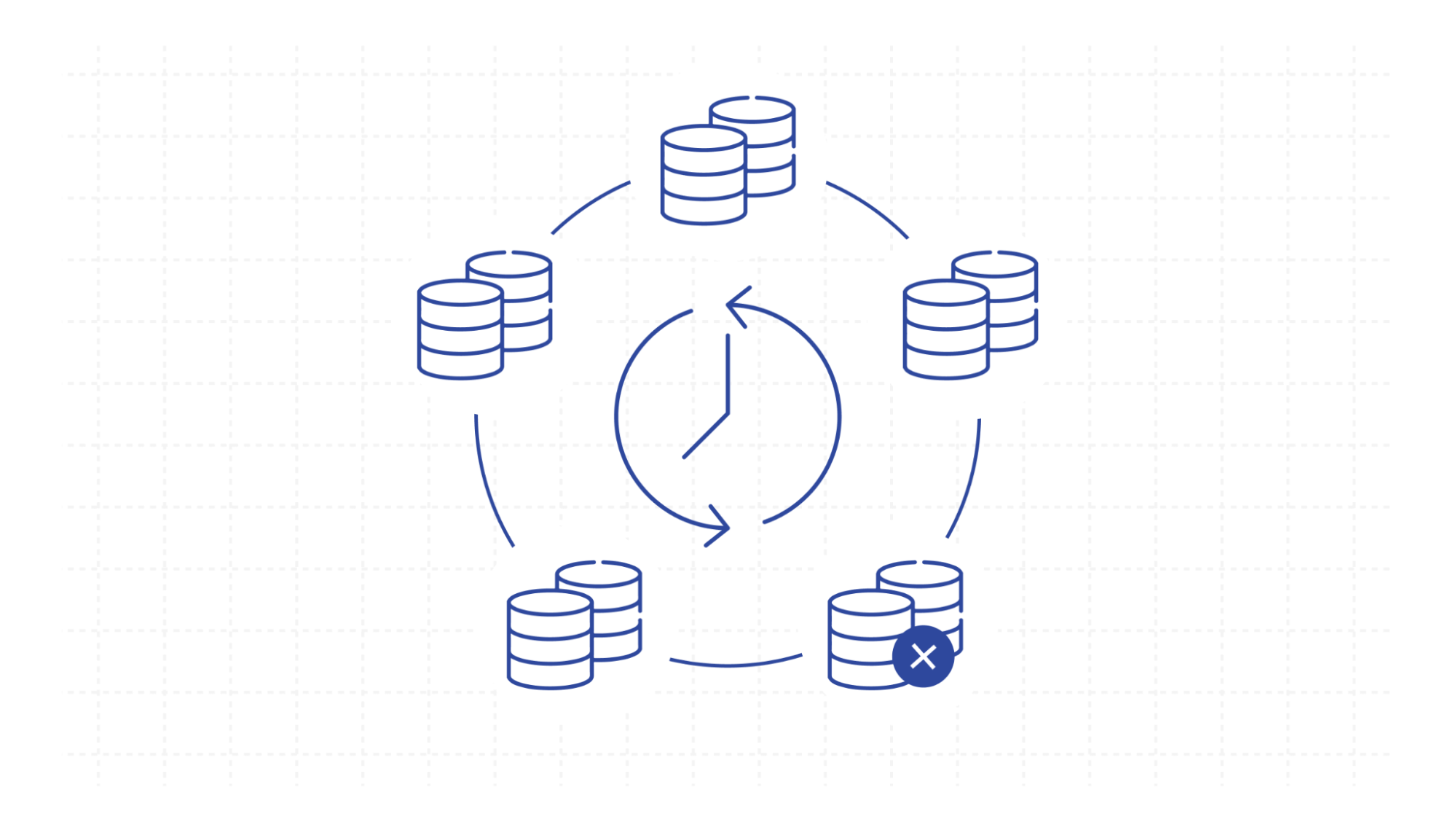
In cell-based architecture Database replication is used to synchronize data between cells to ensure consistency and availability. Changes made to data in one cell need to be propagated to other cells where that data is relevant. Replication mechanisms vary based on the specific database technology used, but they involve replicating data changes asynchronously or semi-synchronously between cells.
When to use Cell Based Architecture?
For systems that require high scalability and the ability to handle large volumes of traffic, cell-based architecture allows for horizontal scaling by adding more cells as needed.
Applications with dynamic workloads that require rapid scaling up or down based on demand, cell-based architecture provides the flexibility to scale individual cells independently, optimizing resource utilization.